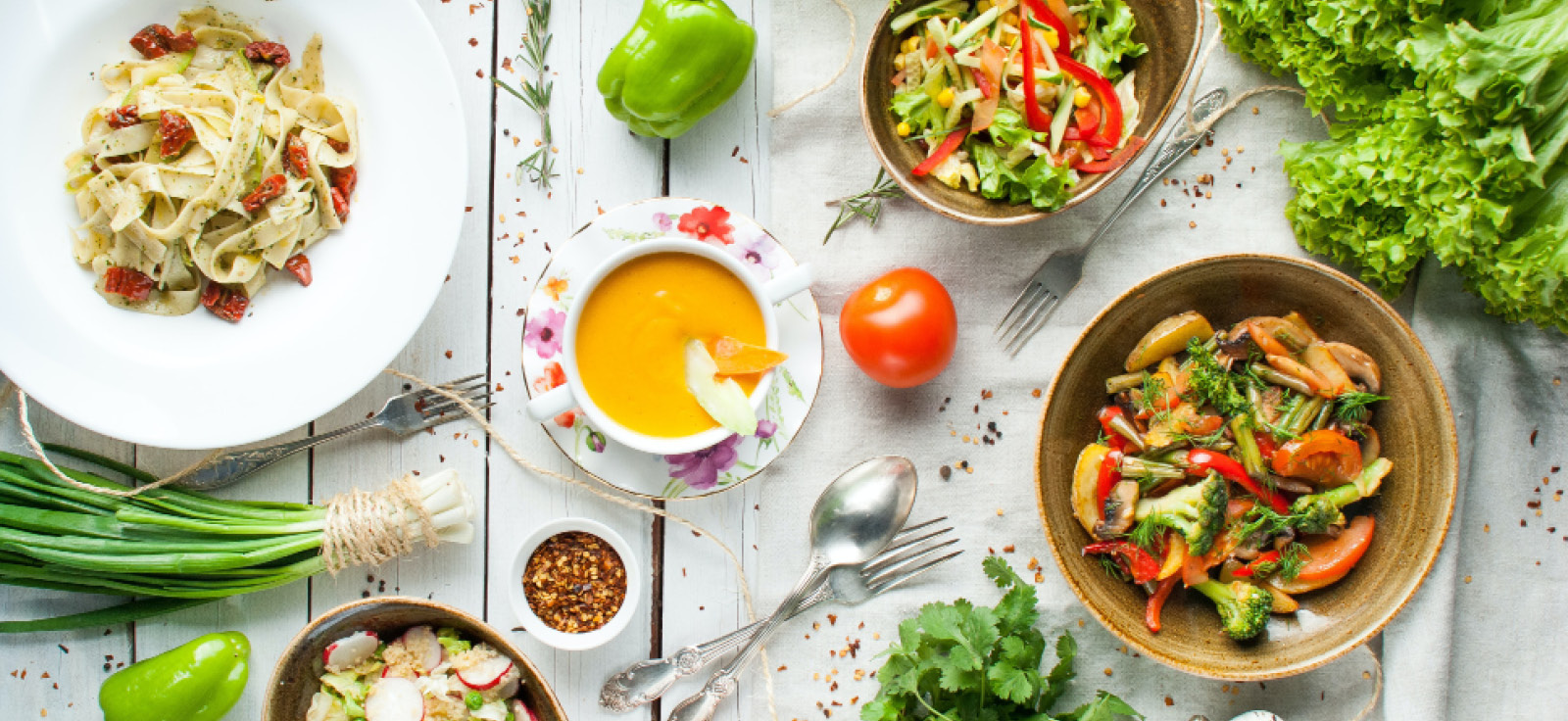
The Vegetarian’s Diet Plan
With Meal Prep Plan to make it Easy Peasy
In recent years, plant-based diets have become increasingly popular among health nuts and newbies. This is because vegetarian diets are associated with several health benefits and an improved diet that is dense in fortified foods, vitamins, and minerals. A well-planned vegetarian diet can also reduce an individual’s risk of chronic disease, support healthy weight loss, and improve the quality of one’s fitness and overall well-being. That said, proper planning is critical to prevent nutritional deficiencies and potential adverse effects on health.
Let’s discuss the vegetarian diet plan with meal prep to make it easy peasy.

What is a Vegetarian Diet?
According to a 2018 Gallup poll, 5 percent of U.S. adults consider themselves to be vegetarian. A vegetarian diet is a dietary plan that excludes all animal products, such as meat, poultry, fish, and eggs. Vegetarians typically consume plant foods such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Some people who follow a vegetarian diet may also abstain from animal by-products, such as honey and gelatin, as well as any food containing animal-based ingredients, such as dairy foods.
Vegetarian diets can be classified into several different types, including lacto-ovo vegetarian, lacto vegetarian and vegan. Lacto-ovo vegetarians include dairy products and eggs in their diet, while lacto vegetarians abstain from eggs and vegan diets exclude all animal products.
Is Vegetarian the Same as Vegan?
Vegetarianism and veganism are two different dietary regimes, and although they both exclude meat from the diet, there are some significant differences between the two.
Vegetarians do not eat meat, poultry, or fish. Instead, they rely on alternative sources of protein, such as legumes, nuts, and grains. They may also consume eggs and dairy products. Vegans, on the other hand, completely avoid all animal products, including eggs and dairy products, and honey. Vegans also avoid animal-derived ingredients, such as gelatin and some food colorings, as well as clothing, personal care products, and other items made from animal by-products, such as leather and wool.
The main difference between vegetarian and vegan diets is that vegans take the practice of avoiding animal products a step further than vegetarians. While vegetarians may still consume milk, eggs, and cheese, vegans avoid all related products. This means that veganism is a much more restrictive diet, and it requires more research and attention to detail than vegetarianism to ensure the individual is getting enough key nutrients and a balanced diet.
The other key difference between vegetarianism and veganism is the motivation behind them. While both diets are based on a love of animals and a desire to reduce animal suffering, vegans tend to be more passionate and outspoken about the cause. They often advocate for animal rights and are willing to go to greater lengths to avoid any animal products, including animal foods, eggs, dairy products, and ground beef.

What are the Associated Health Benefits?
The health benefits of vegetarian diets are often credited to their lower calorie and fat intake compared to non-vegetarian diets. Studies have also indicated that vegetarian diets may reduce the risk of certain cancers, heart disease, and stroke, as well as other chronic diseases. Vegetarian diets may help to reduce cholesterol levels and promote weight loss, as well as help to reduce inflammation, and promote healthy skin and ideal body weight.
Potential to Reduce Risk of Certain Cancers
Research suggests that avoiding animal products, such as red and processed meats, may help to reduce the risk of some types of cancers. This could be due to a variety of factors, such as the lack of hormones, antibiotics, and other potentially harmful substances found in animal products. Additionally, vegetarian diets often include more plant-based foods, which have higher levels of antioxidants, fiber, and other beneficial nutrients, as well as a lower fat content.
One of the most commonly cited studies linking vegetarianism to a reduced risk of cancer is the EPIC-Oxford study, which showed that vegetarians had a lower risk of colorectal cancer than those who ate meat. Other research suggests that vegetarian diets may also help to reduce the risk of other types of cancers, such as breast, prostate, and lung cancer.
Vegetarian diets are typically higher in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals, which can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is believed to be a factor in the development of certain types of cancer. Additionally, vegetarian diets are often lower in saturated fat, which can also help to reduce inflammation.
Finally, vegetarian diets are often higher in proteins, such as beans, which can provide a healthy source of protein that can help to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer. Alternative sources of proteins are also typically lower in calories and higher in essential vitamins and minerals than animal-based proteins.
Potential to Reduce Risk of Obesity
A healthy vegetarian diet has long been touted as a healthy lifestyle, but it is increasingly being viewed as a potential tool to reduce the risk of obesity. Obesity rates are skyrocketing in many parts of the world. In fact, 13 percent of the global population is considered obese. Thankfully, vegetarianism may be a way to combat this growing epidemic. Plant-based eating is often associated with reducing body weight, chronic disease risk, and nutrition concerns.
There are several ways in which a plant-based diet could potentially reduce the risk of obesity. First, vegetarian diets tend to be lower in calories than meat-based diets. A plant-based diet is typically composed of plant-based foods, which are naturally lower in calories than animal products. This means that vegetarians may be able to achieve a caloric deficit more easily than those who eat meat. Additionally, vegetarian and fortified foods are often high in fiber, which can help to keep you feeling full for longer periods of time. This can help to reduce the risk of overeating and therefore reduce the risk of obesity.
Another factor that may reduce the risk of obesity is that plant-based diets often contain fewer processed and unhealthy foods. Vegetarian diets typically emphasize fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which tend to be healthier than processed and fast foods, such as unnatural fruit juice. This can help to reduce the risk of obesity because these foods are low in calories and high in nutrients.
Potential to Reduce Risk of Diabetes
The first reason why a plant-based diet may help to reduce the risk of diabetes is that it typically involves eating more plant-based foods. Plant-based foods are generally low in saturated fat and free of cholesterol, two factors that are known to contribute to the development of diabetes. Additionally, plant-based foods are high in dietary fiber, which can help to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, plant-based diets typically include a variety of different fruits and vegetables, which are a great source of important vitamins and minerals. These vitamins and minerals can help to reduce inflammation in the body, another factor that can contribute to the development of diabetes.
The second reason why a plant-based diet may help to reduce the risk of diabetes is that it typically involves avoiding processed and unhealthy foods. Many foods that are high in saturated fat, sugar, and sodium, such as processed meats and fried foods, are often linked to an increased risk of developing diabetes. By avoiding these types of foods, vegetarians can reduce their overall risk of developing diabetes.
An Increase in Cardiovascular Health
Vegetarianism has become a popular lifestyle choice for many people, with some research suggesting that it may be associated with improved cardiovascular health. A plant-based diet is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular-related complications. This may be due to the fact that vegetarians tend to have a lower body mass index, lower cholesterol levels, and higher levels of antioxidants.
Vegetarians tend to consume more fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants and other beneficial nutrients. Antioxidants play an important role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease by fighting against oxidative damage in the body. Fruits and vegetables are also high in dietary fiber, which can help to keep cholesterol levels in check and reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Furthermore, vegetarians tend to have a lower intake of saturated fats, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
In addition to the beneficial nutrients found in a vegetarian diet, there is also evidence to suggest that a plant-based diet may lower blood pressure levels. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for developing heart disease and stroke, so reducing blood pressure levels can help to reduce this risk. Studies have also found that vegetarian diets are linked to lower levels of LDL cholesterol, which is the “bad” cholesterol that can lead to clogged arteries.
Potential Risks
Individuals considering a vegetarian diet should consult a healthcare professional to ensure their dietary needs are met. “For generally healthy people, I don’t see any reason that eating a vegetarian diet is risky to health,” says Qi Sun, MD, an assistant professor of nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
It is important to note that a plant-based diet can be nutritionally inadequate if not planned properly. “There are potential pitfalls to meatless eating,” Sun shares, but nutrition education and using supplements when needed can help these individuals overcome them.” People who follow vegetarian diets should ensure they get adequate amounts of protein, iron, zinc, Vitamin B12, and other essential nutrients. Taking a multivitamin or other supplements may help ensure that vegetarians meet their nutritional needs.

What is Included in the Vegetarian Diet?
Vegetarianism is a dietary lifestyle that excludes animal products like meat and fish but allows for the consumption of plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, legumes, and plant-derived proteins. A vegetarian diet is not just a lifestyle choice but has been shown to be beneficial to health. Vegetarians generally have lower rates of obesity, heart disease, and cancer, as well as a decreased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Fruits & Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are essential components of a vegetarian diet. Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and are low in calories. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables every day is important in order to get the full range of vitamins and minerals your body needs. Fruits and vegetables are also great sources of antioxidants, which can help protect the body from the damaging effects of free radicals.
Grains, Nuts, & Legumes
Grains are an essential part of a vegetarian diet. Whole grains like oats, barley, quinoa, and brown rice are packed with fiber, vitamins, minerals, and plant-derived proteins. Eating whole grains can help reduce cholesterol levels, stabilize blood sugar levels, and provide your body with a steady energy source.
Nuts and legumes are essential sources of plant-derived proteins and healthy fats in a vegetarian diet. Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and cashews are packed with healthy fats and protein, and are an excellent source of fiber. Legumes like lentils, beans, and peas are also an essential source of protein and fiber, and can help to reduce cholesterol levels.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are an essential part of a vegetarian diet. Healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, and coconuts are packed with essential fatty acids that are important for heart health. Eating various healthy fats can help reduce cholesterol levels, stabilize blood sugar levels, and provide your body with energy.
Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins are a vital part of a vegetarian diet. Plant-derived proteins like tofu, tempeh, seitan, and edamame are packed with essential amino acids that your body needs for optimal health. Proteins can help to increase muscle mass, reduce cholesterol levels, provide your body with energy, and support a healthy immune system.
Example Meal Plan
Here is an example five-day meal plan with plant-based recipes and enough variety to ensure you don’t face a nutritional deficiency.
Day 1
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with fresh berries, almond butter, chia seeds, and almond milk
- Snack: Apple slices with nut butter Lunch: Veggie wrap with hummus, avocado, sprouts, tomato, and spinach
- Snack: Roasted chickpeas
- Dinner: Baked tofu with roasted sweet potatoes and sautéed kale
Day 2
- Breakfast: Green smoothie with spinach, banana, almond milk, and chia seeds
- Snack: Carrots and celery with hummus
- Lunch: Quinoa bowl with black beans, roasted vegetables, and avocado
- Snack: Trail mix with nuts and dried fruit
- Dinner: Lentil curry with cauliflower and brown rice
Day 3
- Breakfast: Avocado toast with tomato and spinach
- Snack: Apple slices with nut butter
- Lunch: Falafel wrap with tahini sauce, cucumber, and tomato
- Snack: Edamame
- Dinner: Veggie stir-fry with tofu and brown rice
Day 4
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with banana, almond butter, and almond milk
- Snack: Carrots and celery with hummus
- Lunch: Lentil soup with kale and quinoa
- Snack: Roasted chickpeas
- Dinner: Baked sweet potato with black beans, salsa, and guacamole
Day 5
- Breakfast: Green smoothie with spinach, banana, almond milk, and chia seeds
- Snack: Trail mix with nuts and dried fruit
- Lunch: Veggie wrap with hummus, avocado, sprouts, tomato, and spinach
- Snack: Apple slices with nut butter
- Dinner: Portobello mushroom burger with sweet potato fries
Plant-based diets have become increasingly popular among health nuts and newbies in recent years. This is because vegetarian diets are associated with several health benefits and an improved diet that is dense in vitamins and minerals. A well-planned vegetarian diet can also reduce an individual’s risk of chronic disease, support healthy weight loss, and improve the quality of one’s fitness and overall well-being. That said, proper planning is critical to prevent nutritional deficiencies and potential adverse effects on health.
Crunch promotes a culture of positivity, inclusivity, and fun with no judgments by providing an environment for all individuals regardless of their health and fitness goals. Find a Crunch gym near you to try our free trial membership, or join Crunch now. We’re here for you – at the gym or at home. Access the best live & on-demand workouts anytime, anywhere with Crunch+. Ready to get sweaty? Try hundreds of workouts for free! Start your free trial now!